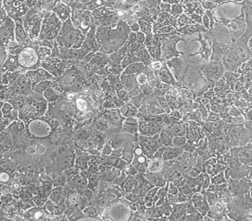
人结肠癌细胞Caco2
BLUEFBIO™ Product Sheet
|
细胞名称 |
人结肠癌细胞Caco2 |
|
|
|
货物编码 |
BFN60800651 |
||
|
产品规格 |
T25培养瓶x1 |
1.5ml冻存管x2 |
|
|
细胞数量 |
1x10^6 |
1x10^6 |
|
|
保存温度 |
37℃ |
-198℃ |
|
|
运输方式 |
常温保温运输 |
干冰运输 |
|
|
安全等级 |
1 |
||
|
用途限制 |
仅供科研用途 1类 |
||
|
培养体系 |
DMEM高糖培养基(Hyclone)+10%胎牛血清(Gibco)+1%双抗(Hyclone) |
||
|
培养温度 |
37℃ |
二氧化碳浓度 |
5% |
|
简介 |
人结肠癌细胞Caco2 细胞分离自一个原发性结肠癌。当细胞长满时,表现出典型的肠细胞分化的特征。Caco-2细胞表达维生素A酸结合蛋白I和视黄醇结合蛋白II,角蛋白阳性。人结肠癌细胞Caco2 细胞由青旗(上海)生物技术发展有限公司于2018年引种自ATCC(HTB-37)。 |
||
|
注释 |
Part of: AstraZeneca Colorectal cell line (AZCL) panel. Part of: Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) project. Part of: ENCODE project common cell types; tier 3. Part of: MD Anderson Cell Lines Project. Doubling time: ~80 hours (DSMZ); ~32 hours (PBCF); ~60-70 hours (CLS). Microsatellite instability: Stable (MSS) (PubMed=24042735; PubMed=25926053; PubMed=28683746). Omics: Deep antibody staining analysis. Omics: Deep exome analysis. Omics: Deep phosphoproteome analysis. Omics: Deep proteome analysis. Omics: Deep RNAseq analysis. Omics: H3K4me3 ChIP-seq epigenome analysis. Omics: H3K27me3 ChIP-seq epigenome analysis. Omics: H3K36me3 ChIP-seq epigenome analysis. Omics: miRNA expression profiling. Omics: N-glycan profiling. Omics: Protein expression by reverse-phase protein arrays. Omics: SNP array analysis. Omics: Transcriptome analysis. |
||
|
STR信息 |
Amelogenin: X CSF1PO: 11 D13S317: 11,13,14 D16S539: 12,13 D5S818: 12,13 D7S820: 11,12 TH01: 6 TPOX: 9,11 vWA: 16,18
|
||
|
参考文献 |
Didier ES, et al. Characterization of Encephalitozoon (Septata) intestinailis isolates cultured from nasal mucosa and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of two AIDS patients. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 43: 34-43, 1996. PubMed: 8563708
Jumarie C, Malo C. Caco-2 cells cultured in serum-free medium as a model for the study of enterocytic differentiation in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 149: 24-33, 1991. PubMed: 1939345
Fogh J, et al. Absence of HeLa cell contamination in 169 cell lines derived from human tumors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 58: 209-214, 1977. PubMed: 833871
Goodfellow M, et al. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 59: 221-226, 1977. PubMed: 77210034
Adachi A, et al. Productive, persistent infection of human colorectal cell lines with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 61: 209-213, 1987. PubMed: 3640832
Trainer DL, et al. Biological characterization and oncogene expression in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 41: 287-296, 1988. PubMed: 3338874
Cohen MB, et al. Receptors for Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin in human intestine and in a human intestinal cell line (Caco-2). J. Cell. Physiol. 156: 138-144, 1993. PubMed: 8100232
Basson MD, et al. Effect of tyrosine kinase inhibition on basal and epidermal growth factor-stimulated human Caco-2 enterocyte sheet migration and proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 160: 491-501, 1994. PubMed: 8077287
Heinen CD, et al. Microsatellite instability in colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines that have full-length adenomatous polyposis coli protein. Cancer Res. 55: 4797-4799, 1995. PubMed: 7585508
Gilbert T, Rodriguez-Boulan E. Induction of vacuolar apical compartments in the Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cell line. J. Cell Sci. 100: 451-458, 1991. PubMed: 1808199
Rigothier MC, et al. A new in vitro model of Entamoeba histolytica adhesion, using the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2: scanning electron microscopic study. Infect. Immun. 59: 4142-4146, 1991. PubMed: 1937772
Levin MS. Cellular retinol-binding proteins are determinants of retinol uptake and metabolism in stably transfected Caco-2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 8267-8276, 1993. PubMed: 8463337
Trotter PJ, Storch J. Fatty acid esterification during differentiation of the human intestinal cell line Caco-2. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 10017-10023, 1993. PubMed: 8387510
Santoro IM, Groden J. Alternative splicing of the APC gene and its association with terminal differentiation. Cancer Res. 57: 488-494, 1997. PubMed: 9012479
White LJ, et al. Attachment and entry of recombinant norwalk virus capsids to cultured human and animal cell lines. J. Virol. 70: 6589-6597, 1996. PubMed: 8794293
Baier LJ, et al. A polymorphism in the human intestinal fatty acid binding protein alters fatty acid transport across Caco-2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 10892-10896, 1996. PubMed: 8631905
Kutchera W, et al. Protaglandin H synthase 2 is expressed abnormally in human colon cancer: evidence for a transcriptional effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 4816-4820, 1996. PubMed: 8643486
Grindstaff KK, et al. Translational regulation of Na,K-ATPase alpha1 and beta1 polypeptide expression in epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 23211-23221, 1996. PubMed: 8798517 |
||
验收细胞注意事项
1、收到人结肠癌细胞Caco2细胞,请查看瓶子是否有破裂,培养基是否漏出,是否浑浊,如有请尽快联系。
2、收到人结肠癌细胞Caco2细胞,如包装完好,请在显微镜下观察细胞。,由于运输过程中的问题,细胞培养瓶中的贴壁细胞有可能从瓶壁中脱落下来,显微镜下观察会出现细胞悬浮的情况,出现此状态时,请不要打开细胞培养瓶,应立即将培养瓶置于细胞培养箱里静止 3-5 小时左右,让细胞先稳定下,再于显微镜下观察,此时多数细胞会重新贴附于瓶壁。如细胞仍不能贴壁,请用台盼蓝染色法鉴定细胞活力,如台盼蓝染色证实细胞活力正常请按悬浮细胞的方法处理。
3、收到人结肠癌细胞Caco2细胞后,请镜下观察细胞,用恰当方式处理细胞。若悬浮的细胞较多,请离心收集细胞,接种到一个新的培养瓶中。弃掉原液,使用新鲜配制的培养基,使用进口胎牛血清。刚接到细胞,若细胞不多时 血清浓度可以加到 15%去培养。若细胞迏到 80%左右 ,血清浓度还是在 10%。
4、收到人结肠癌细胞Caco2细胞时如无异常情况 ,请在显微镜下观察细胞密度,如为贴壁细胞,未超过80%汇合度时,将培养瓶中培养基吸出,留下 5-10ML 培养基继续培养:超过 80%汇合度时,请按细胞培养条件传代培养。如为悬浮细胞,吸出培养液,1000 转/分钟离心 3 分钟,吸出上清,管底细胞用新鲜培养基悬浮细胞后移回培养瓶。
5、将培养瓶置于 37℃培养箱中培养,盖子微微拧松。吸出的培养基可以保存在灭菌过的瓶子里,存放于 4℃冰箱,以备不时之需。
6、24 小时后,人结肠癌细胞Caco2细胞形态已恢复并贴满瓶壁,即可传代。(贴壁细胞)将培养瓶里的培养基倒去,加 3-5ml(以能覆盖细胞生长面为准)PBS 或 Hanks’液洗涤后弃去。加 0.5-1ml 0.25%含 EDTA 的胰酶消化,消化时间以具体细胞为准,一般 1-3 分钟,不超过 5 分钟。可以放入37℃培养箱消化。轻轻晃动瓶壁,见细胞脱落下来,加入 3-5ml 培养基终止消化。用移液管轻轻吹打瓶壁上的细胞,使之完全脱落,然后将溶液吸入离心管内离心,1000rpm/5min。弃上清,视细胞数量决定分瓶数,一般一传二,如细胞量多可一传三,有些细胞不易传得过稀,有些生长较快的细胞则可以多传几瓶,以具体细胞和经验为准。(悬浮细胞)用移液管轻轻吹打瓶壁,直接将溶液吸入离心管离心即可。
7、贴壁细胞 ,悬浮细胞。严格无菌操作。换液时,换新的细胞培养瓶和换新鲜的培养液,37℃,5%CO2 培养。
特别提醒: 原瓶中培养基不宜继续使用,请更换新鲜培养基培养。