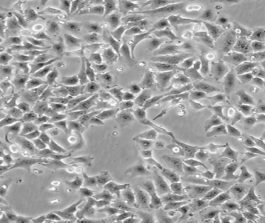
人宫颈癌细胞HeLa
BLUEFBIO™ Product Sheet
|
细胞名称 |
人宫颈癌细胞HeLa |
||
|
货物编码 |
BFN60700111 |
||
|
产品规格 |
T25培养瓶x1 |
1.5ml冻存管x2 |
|
|
细胞数量 |
1x10^6 |
1x10^6 |
|
|
保存温度 |
37℃ |
-198℃ |
|
|
运输方式 |
常温保温运输 |
干冰运输 |
|
|
安全等级 |
1 |
||
|
用途限制 |
仅供科研用途 1类 |
||
|
培养体系 |
DMEM高糖培养基(Hyclone)+10%胎牛血清(Gibco)+1%双抗(Hyclone) |
||
|
培养温度 |
37℃ |
二氧化碳浓度 |
5% |
|
简介 |
HeLa是第一个来自人体组织经连续培养获得的非整倍体上皮样细胞系,它由GeyGO等在1951年从31岁女性黑人的宫颈癌组织建立。经原始组织切片重新观察,Jones等将其诊断为腺癌。已知该细胞系含有人乳头状瘤病毒HPV18序列,需在2级生物安全防护台操作。该细胞角蛋白阳性,p53表达量较低,但表达正常水平的pRB(视网膜母细胞瘤抑制因子)。该细胞引种自ATCC CCL-2。该细胞经过修饰,可高表达cx43,HeLa-CX43在我库中保藏。 |
||
|
注释 |
Group: Space-flown cell line (cellonaut). Part of: Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) project. Part of: COSMIC cell lines project. Part of: MD Anderson Cell Lines Project. Part of: Naval Biosciences Laboratory (NBL) collection (transferred to ATCC in 1982). Characteristics: HeLa has 5 five HPV18 integration sites: three on normal chromosomes 8 at 8q24 and two on derivative chromosomes, der(5)t(5;22;8)(q11;q11q13;q24) and der(22)t(8;22)(q24;q13). Doubling time: 1.3 days (PubMed=29156801); ~48 hours (DSMZ). Microsatellite instability: Stable (MSS) (PubMed=12661003; Sanger). Transformant: NCBI_TaxID; 333761; Human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18). Omics: Cell surface proteome. Omics: CNV analysis. Omics: Deep antibody staining analysis. Omics: Deep exome analysis. Omics: Deep membrane proteome analysis. Omics: Deep phosphoproteome analysis. Omics: Deep proteome analysis. Omics: Deep quantitative proteome analysis. Omics: Deep RNAseq analysis. Omics: DNA methylation analysis. Omics: Genome sequenced. Omics: Glycoproteome analysis by proteomics. Omics: Myristoylated proteins analysis by proteomics. Omics: Protein expression by reverse-phase protein arrays. Omics: SNP array analysis. Omics: Transcriptome analysis. Omics: Virome analysis using proteomics. Anecdotal: The HeLa cell line which was established in February 1951 is the oldest human immortal cell line. Anecdotal: The fascinating story of the HeLa cell line and of Henrietta Lacks from whom these cells originate are described in the book of Rebecca Skloot (CelloPub=CLPUB00377). Anecdotal: The HeLa cell line and its story inspired Australian artist Cynthia Verspaget to embark in 2003 on a artistic project 'The Anarchy Cell Line' (TAnCL) where she mixed her blood with HeLa cells. This work later spawned a PhD thesis (CelloPub=CLPUB00376) where among other things she makes the observation that two main taxonomical distinctions present in the zombie, living/dead and humannhuman, are also present in the HeLa cell line. Anecdotal: Was flown since the 1960s on at least ten different space missions: Korabl-Sputnik-2, Vostok-1, Vostok-4, Vostok-5 and Vostok-6, Voshkod 1 and Zond-5, Discoverer XVIII, Progress M-35/Mir and Shuttle STS-89. Miscellaneous: HeLa is the most frequent contributor to cell lines contamination. |
||
|
STR信息 |
Amelogenin:X;CSF1PO:9,10;D13S317:12,13.3;D16S539:9,10;D18S51:16;D19S433:13,14;D21S11:27,28;D2S1338:17;D3S1358:15,18;D5S818:11,12;D7S820:8,12;D8S1179:12,13;FGA:18,21;TH01:7;TPOX:8,12;vWA:16,18; |
||
|
参考文献 |
PubMed=28601559; DOI=10.1016/j.cels.2017.05.009 Bekker-Jensen D.B., Kelstrup C.D., Batth T.S., Larsen S.C., Haldrup C., Bramsen J.B., Sorensen K.D., Hoyer S., Orntoft T.F., Andersen C.L., Nielsen M.L., Olsen J.V. An optimized shotgun strategy for the rapid generation of comprehensive human proteomes. Cell Syst. 4:587-599.e4(2017)
PubMed=29156801; DOI=10.18632/oncotarget.21174 Kalu N.N., Mazumdar T., Peng S., Shen L., Sambandam V., Rao X., Xi Y., Li L., Qi Y., Gleber-Netto F.O., Patel A., Wang J., Frederick M.J., Myers J.N., Pickering C.R., Johnson F.M. Genomic characterization of human papillomavirus-positive and -negative human squamous cell cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 8:86369-86383(2017)
PubMed=30175587; DOI=10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00392 Robin T., Bairoch A., Muller M., Lisacek F., Lane L. Large-scale reanalysis of publicly available HeLa cell proteomics data in the context of the Human Proteome Project. J. Proteome Res. 17:4160-4170(2018)
PubMed=30787054; DOI=10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-1132 Hooker S.E., Woods-Burnham L., Bathina M., Lloyd S.M., Gorjala P., Mitra R., Nonn L., Kimbro K.S., Kittles R. Genetic ancestry analysis reveals misclassification of commonly used cancer cell lines. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 28:1003-1009(2019)
PubMed=30894373; DOI=10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2747 Dutil J., Chen Z., Monteiro A.N., Teer J.K., Eschrich S.A. An interactive resource to probe genetic diversity and estimated ancestry in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 79:1263-1273(2019)
PubMed=31068700; DOI=10.1038/s41586-019-1186-3 Ghandi M., Huang F.W., Jane-Valbuena J., Kryukov G.V., Lo C.C., McDonald E.R. III, Barretina J., Gelfand E.T., Bielski C.M., Li H., Hu K., Andreev-Drakhlin A.Y., Kim J., Hess J.M., Haas B.J., Aguet F., Weir B.A., Rothberg M.V., Paolella B.R., Lawrence M.S., Akbani R., Lu Y., Tiv H.L., Gokhale P.C., de Weck A., Mansour A.A., Oh C., Shih J., Hadi K., Rosen Y., Bistline J., Venkatesan K., Reddy A., Sonkin D., Liu M., Lehar J., Korn J.M., Porter D.A., Jones M.D., Golji J., Caponigro G., Taylor J.E., Dunning C.M., Creech A.L., Warren A.C., McFarland J.M., Zamanighomi M., Kauffmann A., Stransky N., Imielinski M., Maruvka Y.E., Cherniack A.D., Tsherniak A., Vazquez F., Jaffe J.D., Lane A.A., Weinstock D.M., Johannessen C.M., Morrissey M.P., Stegmeier F., Schlegel R., Hahn W.C., Getz G., Mills G.B., Boehm J.S., Golub T.R., Garraway L.A., Sellers W.R. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature 569:503-508(2019) |
||
验收细胞注意事项
1、收到人宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞,请查看瓶子是否有破裂,培养基是否漏出,是否浑浊,如有请尽快联系。
2、收到人宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞,如包装完好,请在显微镜下观察细胞。,由于运输过程中的问题,细胞培养瓶中的贴壁细胞有可能从瓶壁中脱落下来,显微镜下观察会出现细胞悬浮的情况,出现此状态时,请不要打开细胞培养瓶,应立即将培养瓶置于细胞培养箱里静止 3-5 小时左右,让细胞先稳定下,再于显微镜下观察,此时多数细胞会重新贴附于瓶壁。如细胞仍不能贴壁,请用台盼蓝染色法鉴定细胞活力,如台盼蓝染色证实细胞活力正常请按悬浮细胞的方法处理。
3、收到人宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞后,请镜下观察细胞,用恰当方式处理细胞。若悬浮的细胞较多,请离心收集细胞,接种到一个新的培养瓶中。弃掉原液,使用新鲜配制的培养基,使用进口胎牛血清。刚接到细胞,若细胞不多时 血清浓度可以加到 15%去培养。若细胞迏到 80%左右 ,血清浓度还是在 10%。
4、收到人宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞时如无异常情况 ,请在显微镜下观察细胞密度,如为贴壁细胞,未超过80%汇合度时,将培养瓶中培养基吸出,留下 5-10ML 培养基继续培养:超过 80%汇合度时,请按细胞培养条件传代培养。如为悬浮细胞,吸出培养液,1000 转/分钟离心 3 分钟,吸出上清,管底细胞用新鲜培养基悬浮细胞后移回培养瓶。
5、将培养瓶置于 37℃培养箱中培养,盖子微微拧松。吸出的培养基可以保存在灭菌过的瓶子里,存放于 4℃冰箱,以备不时之需。
6、24 小时后,人宫颈癌细胞HeLa细胞形态已恢复并贴满瓶壁,即可传代。(贴壁细胞)将培养瓶里的培养基倒去,加 3-5ml(以能覆盖细胞生长面为准)PBS 或 Hanks’液洗涤后弃去。加 0.5-1ml 0.25%含 EDTA 的胰酶消化,消化时间以具体细胞为准,一般 1-3 分钟,不超过 5 分钟。可以放入37℃培养箱消化。轻轻晃动瓶壁,见细胞脱落下来,加入 3-5ml 培养基终止消化。用移液管轻轻吹打瓶壁上的细胞,使之完全脱落,然后将溶液吸入离心管内离心,1000rpm/5min。弃上清,视细胞数量决定分瓶数,一般一传二,如细胞量多可一传三,有些细胞不易传得过稀,有些生长较快的细胞则可以多传几瓶,以具体细胞和经验为准。(悬浮细胞)用移液管轻轻吹打瓶壁,直接将溶液吸入离心管离心即可。
7、贴壁细胞 ,悬浮细胞。严格无菌操作。换液时,换新的细胞培养瓶和换新鲜的培养液,37℃,5%CO2 培养。
特别提醒: 原瓶中培养基不宜继续使用,请更换新鲜培养基培养。